
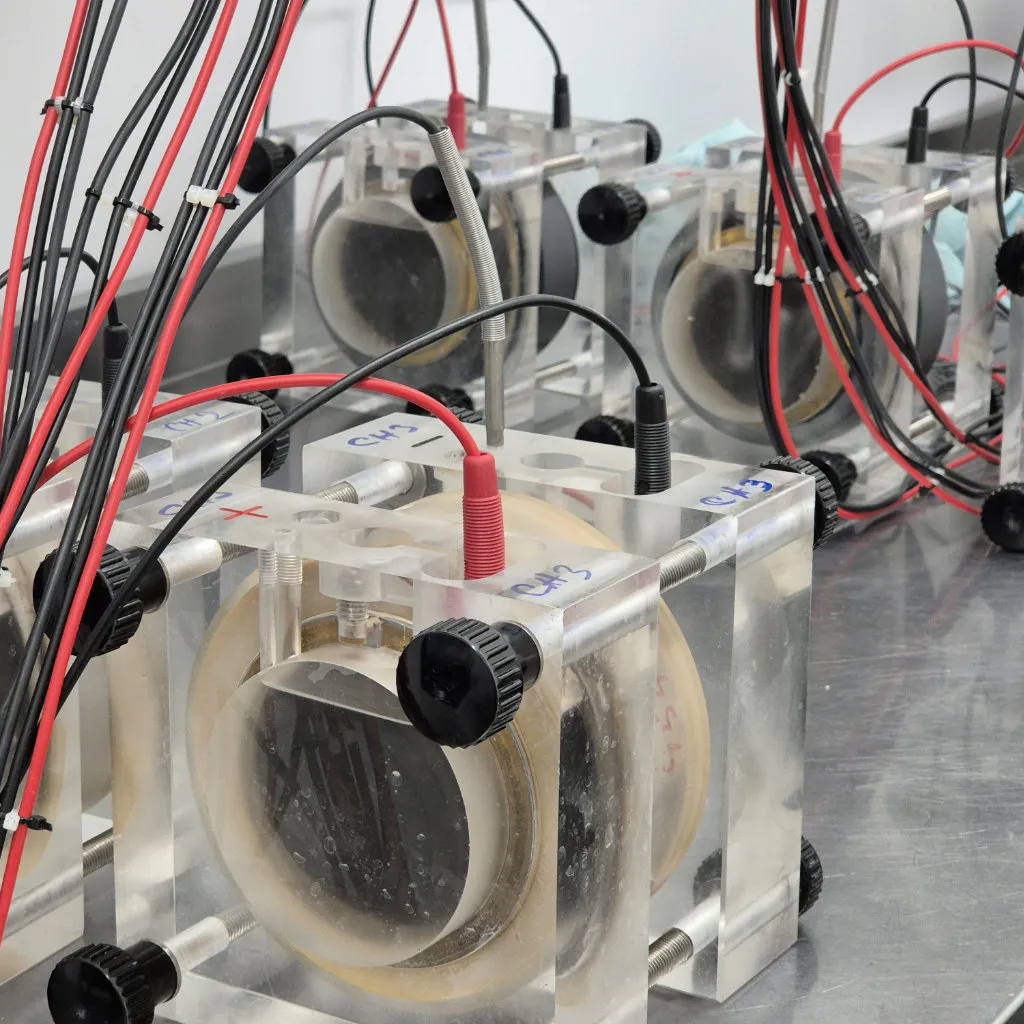
Chloride migration testing determines the chloride migration coefficient in concrete, mortar, or cement-based repair materials, evaluating their resistance to chloride ion penetration. This test is vital for assessing the risk of chloride-induced corrosion, which can weaken reinforced concrete structures over time.
Chloride migration testing is essential for evaluating the long-term durability of concrete and repair materials exposed to chloride, ensuring structural safety and performance in aggressive environments.
AMTEST UK Ltd delivers top-tier services to civil engineering and infrastructure clients across the UK, backed by expert in-house concrete consultants.
Unit A 2D/6, Project Park, North Crescent, London E16 4TQ
Chloride migration testing determines the chloride migration coefficient in concrete, mortar, or cement-based repair materials, evaluating their resistance to chloride ion penetration. This test is vital for assessing the risk of chloride-induced corrosion, which can weaken reinforced concrete structures over time.
Chloride migration testing is essential for evaluating the long-term durability of concrete and repair materials exposed to chloride, ensuring structural safety and performance in aggressive environments.